The impact of the clinical benefits for patients thanks to this new personalised radiotherapeutic treatment option are potentially broad.
Thanks to the targeted and localized direct intratumoural application of YntraDose, not only is the product relatively simple to use, but more importantly, there is the opportunity to reach lesions in a wide range of anatomies and therefore open the door to benefit many solid tumour cancer patient groups worldwide.
 Prof. Jafar Golzarian
Prof. Jafar Golzarian At the very beginning of the history of Interventional Oncology, ethanol injection, the only modality available at that time, was rather impressive, given that with simple percutaneous injections it allowed to achieve outcomes comparable to those of complex surgical procedures, albeit in selected cases. The new technology of YntraDose, using Y-90, seems to be the natural evolution of the old ethanol injection, but applicable in a wide range of neoplastic diseases of different organs, with single applications and greater precision of guidance, given the great progress of imaging modalities. In summary, an actual ‘targeted therapy’ extensively feasible.
 Prof. Luigi Solbiati
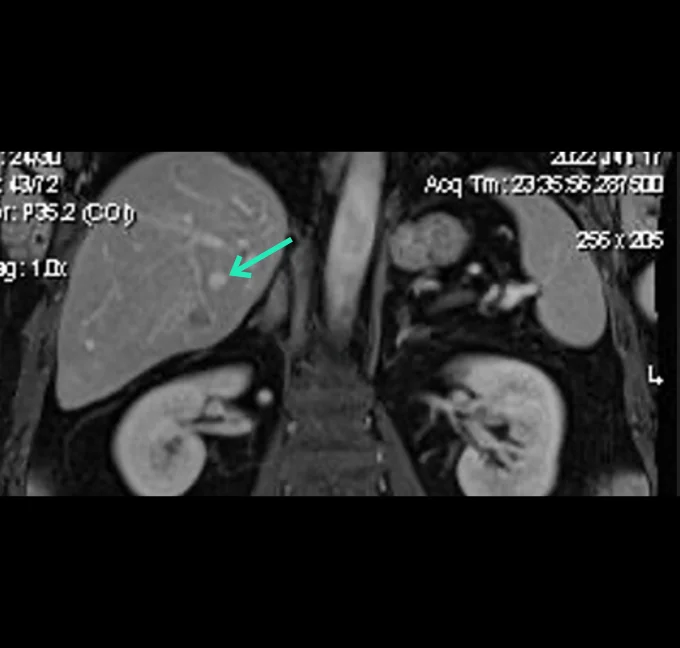
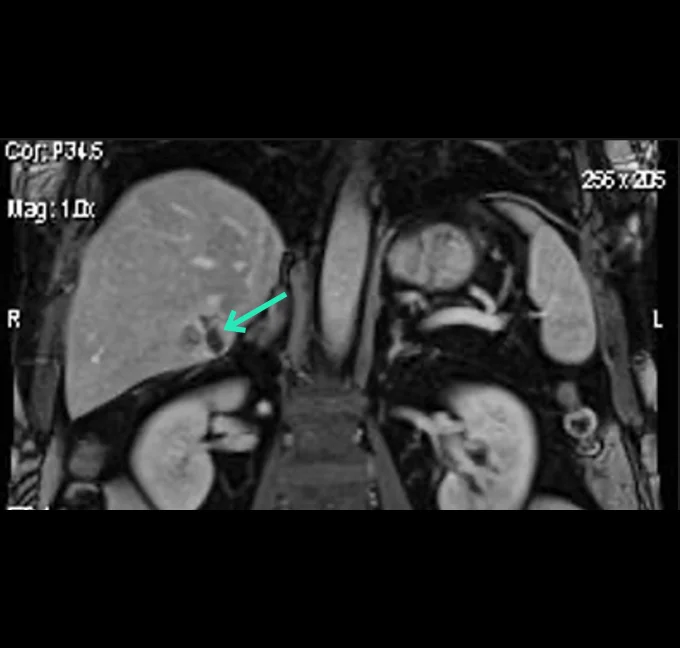
Prof. Luigi Solbiati Clinical data (Hepatocellular Carcinoma)
In an ICH-GCP and ISO14155 compliant clinical investigation, YntraDose has been shown to be safe and well tolerated in a range of unresectable HCC patients. Furthermore, very encouraging effectiveness outcomes at just day 21 post-treatment with YntraDose have been observed. In this setting YntraDose was administered percutaneously directly into the liver lesions under radiological guidance.
Preliminary results from this study were presented as a poster at the GEST 2023 meeting in May 2023 and have subsequently been published as an abstract in JVASC Interv Radiol 2023: 43: e29-e70.